One Complete Guide to Lycopene Health Benefits, and Natural Sources Sources
Introduction
Welcome to our complete guide on Lycopene, the powerful antioxidant. In this blog post, we will explore the chemical structure, properties, health benefits, natural sources, absorption and bioavailability, recommended intakes, potential side effects, and more. Let’s dive in!
What is Lycopene?
It is a natural pigment that belongs to the carotenoid family. It is responsible for the red color found in fruits and vegetables such as tomatoes, watermelon, pink grapefruit, and guava. This powerful antioxidant has gained attention for its potential health benefits.
History and Origins of
Lycopene
Lycopene was first isolated in 1910 by Richard Willstätter and Arthur Stoll. The name “lycopene” derives from the Latin word “lycopersicum,” which means “wolf peach.” Its scientific name is all-trans-lycopene.
In traditional medicine, lycopene has been used for its various health benefits. It has been incorporated into traditional remedies for its potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Contemporary research has supported many of the traditional uses of it, uncovering its potential to promote overall health and well-being.
Health Benefits of Lycopene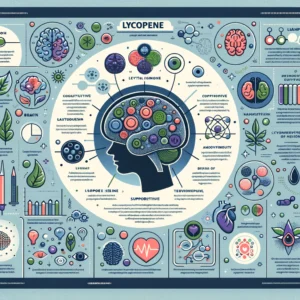
Lycopene has been studied extensively for its potential health benefits. Here are some of the key benefits that have been discovered in recent decades:
1. Powerful Antioxidant
Lycopene acts as a potent antioxidant, helping to protect our cells from damage caused by harmful free radicals. By neutralizing these free radicals, it may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, certain cancers, and age-related macular degeneration.
2. Cardiovascular Health
Studies have shown that it may have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. It may help lower LDL cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve blood vessel function. These effects contribute to a lower risk of heart disease and stroke.
3. Prostate Health
Lycopene has been extensively studied for its potential role in promoting prostate health. Research suggests that it may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer and slow down the progression of the disease in men who have been diagnosed.
4. Skin Protection
It has shown promise in protecting the skin from damage caused by UV radiation. It may help reduce the risk of sunburn and skin aging, as well as provide some defense against skin cancer.
Natural Sources of Lycopene
It is naturally found in various fruits and vegetables. Some of the best sources include:
1. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are one of the richest sources of lycopene. Cooking tomatoes increases the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for our bodies to absorb.
2. Watermelon
Watermelon is another delicious source of lycopene. Its refreshing taste makes it a popular choice during the summer months.
3. Pink Grapefruit
Pink grapefruit not only provides a tangy and sweet flavor but also contains a good amount of lycopene.
4. Guava
Guava is a tropical fruit that is packed with it. It can be enjoyed on its own or added to smoothies and salads.
Lycopene Absorption and Bioavailability
The absorption and bioavailability of it can be influenced by various factors:
1. Fat Solubility
Lycopene is a fat-soluble compound, which means it is better absorbed when consumed with a source of healthy fats, such as olive oil or avocado.
2. Processing and Cooking
Cooking tomatoes and processing them into sauces or pastes can increase the bioavailability of it. However, excessive heat and prolonged cooking times may lead to some degradation of lycopene.
3. Interactions with Other Compounds
Its absorption can be influenced by other dietary compounds, such as fiber and certain antioxidants. Consuming lycopene-rich foods as part of a balanced diet can enhance its absorption.
Recommended Intakes of Lycopene
There are currently no specific dietary guidelines for lycopene intake. However, incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet regularly can provide you with its potential health benefits.
If you are considering lycopene supplements or extracts, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your individual needs.
Potential Side Effects and Safety
Lycopene is generally recognized as safe when consumed in food amounts. However, high doses of lycopene supplements may cause some side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or temporary discoloration of the skin known as lycopenodermia.
It is important to note that lycopene supplements may interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners. If you are taking any medications, it is advisable to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can lycopene prevent or cure cancer?
A: While it has shown potential in reducing the risk of certain cancers, it is not a cure for cancer. It is important to maintain a balanced diet and follow appropriate medical advice for cancer prevention and treatment.
Q: Can lycopene replace sunscreen?
A: No, it should not be used as a replacement for sunscreen. While it may offer some protection against UV radiation, it is always recommended to use sunscreen to protect your skin from harmful sun exposure.
References
1. Rao AV, Agarwal S. Role of lycopene as antioxidant carotenoid in the prevention of chronic diseases: a review. Nutr Res. 1999;19(2):305-323.
2. Gajendragadkar PR, Hubsch A, Mäki-Petäjä KM, et al. Effects of oral lycopene supplementation on vascular function in patients with cardiovascular disease and healthy volunteers: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99070.
Sources
1. National Institutes of Health. Lycopene. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Lycopene-HealthProfessional/
2. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The Nutrition Source: Lycopene. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/lycopene/
We hope this complete guide to lycopene has provided you with valuable information about this powerful antioxidant. Remember to include lycopene-rich foods in your diet and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Stay healthy!
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or lifestyle
















